Customer Journey Map Examples: 5 Worked Templates by Industry
Customer journey map examples across SaaS, e-commerce, healthcare, financial services, and hospitality. Filled-in stages, touchpoints, and pain points.
The difference between a useful customer journey map and a generic one is specificity. As McKinsey's research on customer journeys confirms, a map that lists "Awareness, Consideration, Purchase" with no touchpoints, no emotional data, and no pain point metrics is a diagram, not a diagnostic tool.
This guide provides five complete customer journey map examples -- filled in with realistic touchpoints, emotions, pain points, and improvement opportunities -- across B2B SaaS, e-commerce, healthcare, financial services, and hospitality. After mapping customer journeys across 80+ CX transformation and go-to-market engagements, we have found that teams learn faster from worked examples than from blank templates. Each example below identifies the "moments of truth" that separate customer loyalty from churn. For the methodology behind building these maps from scratch, see our guide on customer journey mapping. For the broader framework toolkit, see the Strategic Frameworks Guide.
Choosing the Right Customer Journey Map Format#
Before diving into examples, it helps to understand which format fits which situation. Not every journey map looks the same.
| Format | Structure | Best For | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear journey map | Sequential stages left to right | First-time mapping, simple purchase journeys | Cannot capture loops or repeat behaviors |
| Circular journey map | Stages form a loop (advocacy feeds back to awareness) | Subscription businesses, loyalty programs | Harder to pinpoint start/end for analysis |
| Service blueprint | Customer journey + frontstage/backstage operations | Aligning internal processes to CX improvements | Requires deep operational knowledge; takes 2-4 days |
| Experience map | Broad day-in-the-life view beyond your product | Understanding unmet needs and context | Less actionable for specific product improvements |
The five examples below use the linear format because it is the most common starting point. Once you have a linear map, you can extend it into a service blueprint or circular model as the analysis matures.
Customer Journey Map Examples by Industry#
Each example includes the full journey stages, key touchpoints, customer emotions, pain points, and improvement opportunities. For a blank version to fill in with your own data, use the Customer Journey Map Template.
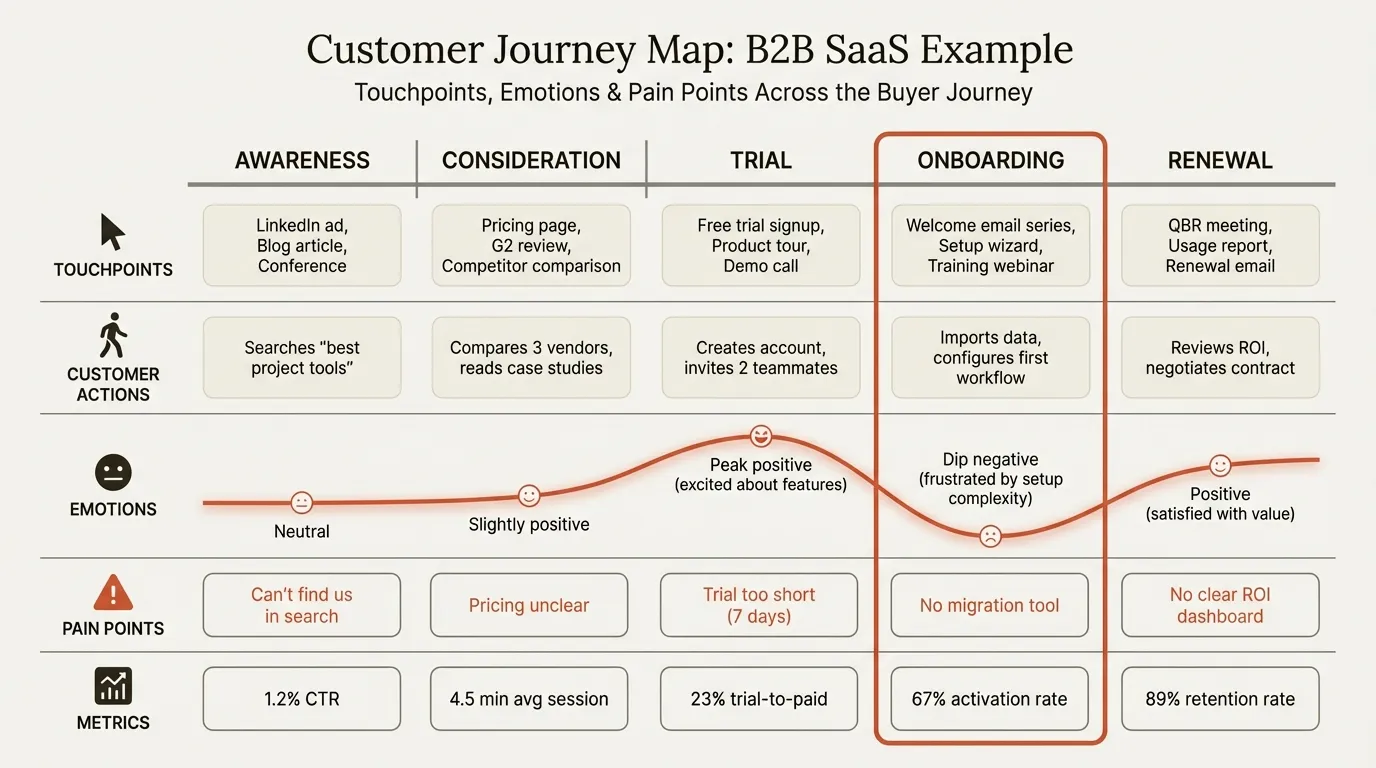
Example 1: B2B SaaS Onboarding (Project Management Platform)#
Context: A Series B project management tool with $22M ARR. The company has strong acquisition metrics but loses 34% of new users within the first 14 days. This map focuses on the post-signup onboarding journey.
| Stage | Touchpoints | Customer Emotion | Pain Points | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sign-up | Website pricing page, free trial form, confirmation email | Hopeful, slightly impatient | Trial requires credit card; 23% abandon at this step | Remove credit card gate; A/B test showed 41% lift in trial starts |
| First login | Welcome screen, product tour, empty dashboard | Overwhelmed, uncertain | 5-step onboarding wizard covers features, not outcomes; users skip it | Replace feature tour with "Set up your first project in 3 minutes" goal-based flow |
| Team invite | In-app invite modal, email invitation, teammate landing page | Motivated but anxious | Invite email has 31% open rate; lands in spam for corporate accounts | Add calendar/Slack integration as alternative invite channel |
| First workflow | Template gallery, task creation, status board | Engaged if successful, frustrated if stuck | Users who do not create a task within 48 hours churn at 3.2x the rate | Trigger proactive in-app message at 24 hours with pre-built template |
| Week 2 activation | Usage dashboard, feature discovery, support chat | Confident or disengaged | Power users adopt 6+ features; churning users average 1.8 features | Segment users by day-3 behavior; route low-engagement cohort to CSM outreach |
Moment of truth: The first workflow stage. Users who complete their first project task within 48 hours retain at 78% after 90 days. Users who do not drop to 24%. Every improvement to this single stage has more ROI than optimizing all other stages combined.
Example 2: E-Commerce Purchase Journey (Premium Skincare Brand)#
Context: A DTC skincare brand with $8.4M annual revenue selling through their website and Amazon. Average order value is $67. Customer acquisition cost has risen 42% in 18 months, making retention critical.
| Stage | Touchpoints | Customer Emotion | Pain Points | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Instagram ad, influencer review, Google search, TikTok | Curious, skeptical of claims | Ad creative shows results but no timeline; sets unrealistic expectations | Add "Results timeline: 4-6 weeks" to all paid creative |
| Consideration | Product pages, ingredient lists, reviews, quiz tool | Interested but confused | 4.2-star average rating, but top negative review ("broke me out") appears first | Reorder reviews by "most helpful"; add skin-type filter to review display |
| Purchase | Cart, checkout, payment, order confirmation | Committed, expecting fast delivery | Checkout requires account creation; 28% cart abandonment at registration step | Enable guest checkout; capture email via post-purchase follow-up instead |
| Delivery & unboxing | Shipping notification, tracking page, package arrival | Excited, evaluating quality | Average delivery time 5.2 days; competitors offer 2-day at same price point | Negotiate 3-day shipping tier; add tracking SMS notifications |
| Usage & results | Product use, results tracking, email follow-ups | Hopeful then either satisfied or disappointed | No guidance on application routine; 18% of support tickets are "how to use" questions | Ship product with QR code linking to 60-second application video |
| Repurchase/advocacy | Reorder reminder email, referral program, review request | Loyal if results visible, indifferent if not | Reorder email sent at day 30; product lasts 45 days for most users | Shift reorder trigger to day 38 based on usage data; include before/after prompt |
Moment of truth: The usage and results stage. The customer's experience during weeks 2-4 determines whether they become a repeat buyer or a one-time purchaser. Support data shows customers who receive application guidance within the first 3 days repurchase at 2.1x the rate of those who do not.
Example 3: Healthcare Patient Experience (Orthopedic Surgery)#
Context: A regional healthcare system with 4 hospitals tracking patient satisfaction for elective orthopedic procedures. HCAHPS scores are in the 62nd percentile -- above average but below the 75th percentile target tied to value-based reimbursement bonuses.
| Stage | Touchpoints | Customer Emotion | Pain Points | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptom & referral | Primary care visit, referral call, insurance pre-auth | Anxious, uncertain about severity | Average 11 days between referral and first specialist appointment; 15% of patients seek a second opinion elsewhere during the wait | Offer telehealth triage within 48 hours of referral to reduce wait anxiety |
| Consultation | Specialist appointment, imaging, diagnosis discussion | Fearful, seeking reassurance | Surgeon spends avg 8 minutes on treatment options; patients report feeling rushed | Provide written treatment comparison sheet; add 15-min nurse follow-up call |
| Pre-surgery prep | Pre-op appointment, paperwork, insurance coordination | Stressed, logistics-focused | 4 separate forms requiring redundant information; patients average 45 minutes on paperwork | Consolidate to single digital intake form pre-populated from EHR |
| Surgery & recovery | Admission, procedure, post-anesthesia, hospital stay | Vulnerable, dependent | Pain management communication inconsistent; 22% of patients report pain not addressed promptly | Implement standardized pain check-in protocol every 2 hours with documented response |
| Discharge & rehab | Discharge instructions, PT referral, follow-up scheduling | Overwhelmed, uncertain about next steps | Discharge paperwork averages 12 pages; 38% of patients call within 72 hours with questions already answered in discharge materials | Replace paper packet with 3-minute video summary; text follow-up at 24/48/72 hours |
| Recovery & outcomes | PT sessions, follow-up appointments, outcome surveys | Progressively confident or frustrated | 27% of patients miss first PT appointment; strong correlation with slower recovery | Automated PT scheduling at discharge with calendar integration and reminder sequence |
Moment of truth: Discharge. The transition from hospital to home is where HCAHPS scores diverge most dramatically. Patients who receive a follow-up call within 24 hours of discharge rate their overall experience 18 points higher than those who do not. This single touchpoint has the strongest correlation with the system's reimbursement-linked satisfaction targets.
Example 4: Financial Services (Mortgage Application)#
Context: A mid-size bank processing 3,200 mortgage applications annually. Net Promoter Score for the mortgage process is 12 -- well below the 34 industry average. The journey from application to closing averages 47 days versus the 38-day target.
| Stage | Touchpoints | Customer Emotion | Pain Points | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research & pre-qualification | Website rate calculator, pre-qualification form, initial call | Hopeful, comparing options | Rate calculator requires 14 fields; competitors offer 3-field instant estimates | Build simplified "estimate in 60 seconds" tool; capture full details later |
| Application | Online application, document upload, loan officer assignment | Committed but overwhelmed | Application asks for 23 documents; no clarity on which are needed immediately vs. later | Stage document requests: 5 critical docs at application, remainder after initial approval |
| Processing & underwriting | Document review, appraisal, title search, underwriting | Anxious, feeling out of control | Average 8 days of silence between application submission and first status update | Automated status updates every 48 hours; assign dedicated loan officer within 24 hours |
| Conditional approval | Approval letter, conditions list, additional document requests | Relieved then frustrated | 62% of applications receive 3+ rounds of "just one more document" requests | Pre-screen for common conditions at application stage; batch condition requests |
| Closing | Final review, closing disclosure, signing, funding | Eager to finish, confused by paperwork | Closing disclosure arrives 2 days before closing with unexpected fees in 31% of cases | Deliver preliminary closing estimate at conditional approval; flag any fee changes proactively |
Moment of truth: The processing and underwriting stage. The silence between application and first update is where NPS collapses. Customer interviews reveal the primary emotion is not frustration with speed -- it is anxiety from uncertainty. Borrowers who receive proactive updates (even "no news yet, still on track") score 22 NPS points higher than those left waiting. The fix costs almost nothing to implement.
Example 5: Restaurant & Hospitality (Fine Dining)#
Context: A 120-seat fine dining restaurant in a major metro area. Average check is $142 per person. Yelp rating is 4.1 stars with consistent complaints about pacing and reservation friction despite strong food quality scores.
| Stage | Touchpoints | Customer Emotion | Pain Points | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery & reservation | Google search, Yelp reviews, OpenTable, restaurant website | Excited, planning a special occasion | Website shows no availability; OpenTable shows 3 slots. Guests feel the restaurant is hard to book | Sync inventory in real-time; add waitlist with estimated availability |
| Arrival & seating | Valet/parking, host greeting, wait area, table assignment | Anticipating, slightly nervous | 40% of parties seated 10+ minutes past reservation time; no communication about delay | Text guests 15 minutes before reservation with status; offer drink at bar if table is delayed |
| Ordering & dining | Menu presentation, server interaction, food delivery, wine service | Engaged, evaluating value | Server visits average 6 per meal; guests report feeling either neglected or interrupted | Train servers on read-the-table cadence; reduce unprompted check-ins from 6 to 3-4 |
| Bill & departure | Check presentation, payment, coat check, exit | Satisfied or deflated depending on pacing | Average 11 minutes between requesting the check and receiving it; 23% of negative reviews mention this | Offer tableside payment via QR code; present check within 3 minutes of request |
| Post-visit | Review prompt, loyalty program, follow-up email | Reflective, deciding whether to return | No follow-up for first-time guests; 68% of new diners do not return within 12 months | Send personalized thank-you email within 24 hours with incentive for second visit |
Moment of truth: Bill and departure. Fine dining guests tolerate a slow start (it feels luxurious), but a slow ending feels disrespectful of their time. The 11-minute average check wait erases goodwill built over a 2-hour meal. Restaurants that reduce check-to-departure time to under 5 minutes see a 0.3-star average improvement on review platforms.
Continue reading: Agenda Slide PowerPoint · Flowchart in PowerPoint · Pitch Deck Guide
Free consulting slide templates
SWOT, competitive analysis, KPI dashboards, and more — ready-made PowerPoint templates built to consulting standards.
Identifying Moments of Truth Across Customer Journey Map Examples#
Every example above contains a single stage where the experience disproportionately determines the overall outcome. These moments of truth share three characteristics:
High emotional stakes. As Forrester's CX research has demonstrated, the customer is vulnerable, uncertain, or making a decision they cannot easily reverse. The SaaS user deciding whether the product is worth learning. The mortgage applicant waiting in silence. The patient leaving the hospital.
Measurable divergence. At these stages, the data splits cleanly between customers who continue and those who leave. The 48-hour activation window in SaaS. The 24-hour post-discharge call in healthcare. The check wait time in hospitality. If you can measure the split, you can prove the investment case for fixing it.
Disproportionate ROI. Improving a moment of truth typically costs less and delivers more than spreading improvement budget across all stages equally. The financial services example -- adding automated status updates -- requires minimal technical investment but addresses the primary driver of a 22-point NPS gap.
To identify moments of truth in your own journey map, look for stages where:
- Drop-off or churn rates spike
- Support ticket volume concentrates
- NPS or satisfaction scores diverge most from adjacent stages
- Customer verbatims use emotional language ("frustrated," "confused," "abandoned")
For frameworks on prioritizing which pain points to address first, stakeholder mapping helps align organizational decision-makers around the improvement roadmap.
From Customer Journey Map Examples to Your Own Map#
These five examples demonstrate that journey maps are only as useful as the specificity they contain. Generic stages produce generic insights. Filled-in touchpoints with measurable pain points produce actionable improvement backlogs.
Key principles from these examples:
- Every pain point needs a number. "Slow checkout" is an observation. "28% cart abandonment at the registration step" is a business case.
- Emotions are data, not decoration. The emotional layer reveals why customers leave, not just where. Anxiety during silence is different from frustration with speed -- and the fix is different too.
- One moment of truth matters more than five incremental improvements. In every example above, a single stage drives the majority of the outcome variance. Find yours before optimizing everything equally.
- The map is a living document. Customer behavior shifts, competitors change the baseline, and new channels emerge. Revisit quarterly.
For the methodology behind building these maps in a workshop setting, see our full guide on customer journey mapping. For a ready-to-use starting point, the Customer Journey Map Template provides a structured layout you can customize in PowerPoint. And for adjacent frameworks that complement journey mapping -- especially stakeholder mapping and business model canvas examples -- see our Strategic Frameworks Guide.
Build consulting slides in seconds
Describe what you need. AI generates structured, polished slides — charts and visuals included.
Try Free