Brainstorming Template: 6 Structured Methods That Produce Real Ideas
Brainstorming templates for mind mapping, brainwriting, SCAMPER, reverse brainstorming, and more. Comparison table, facilitation tips, and workshop guide.
Most brainstorming sessions fail not because the participants lack creativity but because the session lacks structure. As Alex Osborn outlined in his original brainstorming rules in Applied Imagination (1953), "let's think of ideas" produces shallow suggestions, groupthink, and a list that no one acts on.
A good brainstorming template imposes constraints that paradoxically produce better ideas. After facilitating 50+ strategy workshops, we have found six methods cover virtually every ideation scenario. Below, we walk through each with real case studies showing how structured brainstorming produces measurable outcomes. For the broader strategic toolkit, see our Strategic Frameworks Guide.
What Makes a Brainstorming Template Effective#
A brainstorming template separates divergent thinking (generating ideas) from convergent thinking (evaluating them), ensures equal participation, and produces organized output that feeds directly into decision-making. Research on facilitated ideation shows clear patterns: sessions with 6-8 participants generate 40% more viable ideas than sessions with 12 or more, timeboxed phases of 5-7 minutes produce 2.3 times more unique ideas than open-ended formats, and silent-first ideation generates 27% fewer duplicates.
Effective templates share three properties:
| Property | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Timeboxed phases | Each step has a fixed duration | Prevents rabbit holes and maintains energy |
| Silent-first input | Individual ideation precedes group discussion | Eliminates anchoring bias from dominant voices |
| Structured output | Ideas land in a defined format (cards, rows, clusters) | Makes prioritization possible without re-processing |
Without these properties, brainstorming defaults to whoever speaks first and loudest -- which is how most corporate ideation sessions operate, and why most of them produce mediocre results.
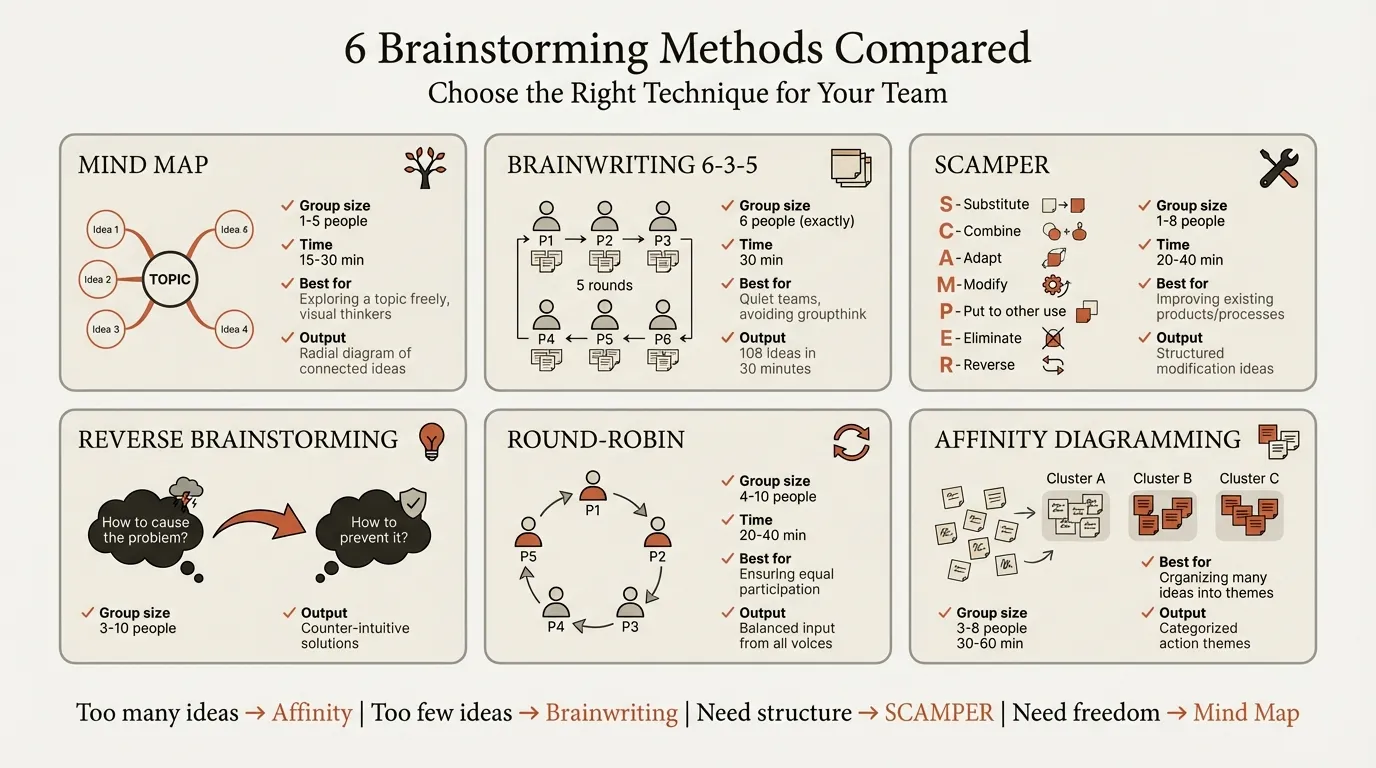
6 Brainstorming Methods With Templates#
1. Mind Mapping#
Mind mapping starts with a central concept and branches outward through associations. Draw 4-6 primary branches for major categories, add secondary branches for sub-ideas, and look for connections across branches -- these cross-branch links often produce the strongest insights.
Best for: Problem decomposition, exploring a topic's full scope, solo or pair ideation. For a ready-made layout, see our Mind Map Template.
2. Brainwriting (6-3-5 Method)#
Brainwriting is the single best method for eliminating groupthink in larger teams. The 6-3-5 format means 6 participants, 3 ideas each, 5 minutes per round. After each round, sheets rotate so participants build on each other's ideas. The output: 108 idea entries from 6 people in 30 minutes.
Best for: Groups of 6-18, politically sensitive topics, situations where hierarchy might suppress honest input.
Case Study: Brainwriting for Consumer Goods Product Line Extension
A snack food company needed to extend its protein bar line beyond gym-goers into mainstream retail. The innovation team ran a brainwriting session with 3 participants from R&D, marketing, and sales. The first 3 rounds:
| Round | Participant A (R&D) | Participant B (Marketing) | Participant C (Sales) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plant-based kids' bar with hidden vegetables | Co-branded bar with a coffee chain | Snack-size 100-calorie format for vending machines |
| 1 | Collagen-infused beauty bar for women 25-40 | Subscription "flavor of the month" club | Bulk 20-pack for Costco warehouse channel |
| 1 | High-fiber digestive health bar for 50+ adults | Limited-edition seasonal flavors (pumpkin, peppermint) | Single-serve at checkout counters under $2 |
| 2 | Build on coffee co-brand: add caffeine + L-theanine for "focus bar" | Build on kids' bar: lunchbox-size with trading cards in wrapper | Build on subscription: corporate wellness box for offices |
| 2 | Build on vending format: pair with existing protein shake as combo | Build on collagen bar: partner with beauty influencers for launch | Build on seasonal: "destination" flavors tied to travel retail |
| 3 | Build on wellness box: add personalized macros via quiz | Build on focus bar: "morning commute" bar with coffee flavor | Build on beauty bar: pharmacy channel placement next to supplements |
After 6 full rounds, the team had 54 entries. They ran affinity clustering and grouped the entries into 7 themes:
- Functional wellness (focus, beauty, digestive) -- 14 entries
- Channel-specific formats (vending, checkout, warehouse) -- 11 entries
- Kids and family -- 8 entries
- Subscription and D2C -- 7 entries
- Co-branding partnerships -- 6 entries
- Seasonal and limited edition -- 5 entries
- Corporate and B2B -- 3 entries
The team advanced Functional wellness and Channel-specific formats to consumer testing. The "focus bar" (caffeine + L-theanine, morning commute positioning) tested at 73% purchase intent among urban professionals 25-34 -- above the 45% launch threshold. The checkout format tested at 61% impulse-buy intent. Both launched within 9 months, contributing $4.2M in incremental first-year revenue.
3. SCAMPER#
SCAMPER is a checklist-based technique that works best when you have an existing product, process, or service to improve. Each letter represents a different lens: Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse. Spend 3-5 minutes per trigger, generating at least 2 ideas before moving on.
Best for: Product improvement, process optimization, incremental innovation. Less effective for blank-slate problems.
Case Study: SCAMPER for SaaS Pricing Model Redesign
A B2B analytics platform ($8M ARR) was losing deals to competitors with flexible pricing. Their three fixed tiers (Starter $49/mo, Pro $149/mo, Enterprise $499/mo) forced mid-market prospects to overpay or outgrow Pro within months. The product team ran SCAMPER on the pricing model:
| SCAMPER Trigger | Ideas Generated | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Substitute | Replace fixed tiers with usage-based pricing (per query, per dashboard, per data source). Substitute annual contracts with monthly rolling. | Usage-based removes the "cliff" between tiers -- customers pay proportionally to value received |
| Combine | Bundle analytics with data warehousing. Combine Pro + Enterprise into a single plan with add-on modules. | Modular add-ons let customers build their own tier |
| Adapt | Borrow AWS's "pay for what you use" model. Adapt Spotify's freemium-to-family plan structure for team licensing. | Per-seat plus per-usage hybrid mirrors how customers actually scale |
| Modify | Shrink the minimum commitment from annual to quarterly. Magnify the free trial from 14 to 45 days. | Longer trial increased conversion by 22% in a later A/B test |
| Put to another use | Use pricing as a lead-gen tool (free tier with watermarked exports). Position entry plan as a "data literacy" tool for non-analysts. | Reframing the entry tier expanded the addressable market |
| Eliminate | Remove the free tier entirely -- it attracted non-buyers who consumed support resources. Eliminate per-seat pricing for the base plan. | Free tier users converted at only 2.1%, but consumed 34% of support tickets |
| Reverse | Let customers set their own price within guardrails (name-your-price pilot). Reverse the upsell flow: start everyone on full-feature trial, then downgrade. | Full-feature trial with downgrade created stronger anchoring to the premium experience |
The two most impactful ideas came from Substitute and Eliminate. The team replaced fixed tiers with a $99/month base fee plus $0.02-per-query usage pricing, and eliminated the free tier in favor of a 45-day full-feature trial. Within two quarters: average contract value increased 31% (from $1,788 to $2,342 annually), mid-market close rate improved from 18% to 29%, support tickets dropped 41%, and net revenue retention climbed from 94% to 112% as customers expanded usage without hitting tier ceilings.
4. Reverse Brainstorming#
Reverse brainstorming asks "how could we make this problem worse?" instead of "how do we solve it?" This inversion breaks conventional thinking patterns and surfaces risks and failure modes that direct brainstorming misses.
Best for: Risk identification, quality improvement, breaking through creative blocks when direct brainstorming stalls.
Case Study: Reverse Brainstorming to Reduce Customer Churn
A mid-market HR software company faced 6.2% monthly churn -- well above the 3-4% SaaS benchmark. Direct brainstorming had produced obvious ideas (better onboarding, more features) but none moved the needle. The VP of Customer Success ran a reverse session with 7 participants: "How could we guarantee every customer cancels within 90 days?"
They generated 23 "ways to make churn worse." The top entries and inversions:
| How to Make Churn Worse | Inverted Solution | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Never follow up after onboarding -- let customers figure it out alone | Implement structured 30/60/90-day check-in sequence with dedicated CSM | High |
| Make the product so complex that only power users survive | Create role-based simplified views (HR admin vs. employee vs. executive) | High |
| Bury the cancellation reason -- never learn why people leave | Add exit survey with 5-question diagnostic; route "fixable" cancellations to a save team | High |
| Only show ROI data to the buyer, not end users | Build employee-facing dashboard showing time saved on HR tasks | Medium |
| Ensure every renewal is a surprise invoice | Send 60-day renewal preview with usage report and value summary | Medium |
| Ship features nobody asked for instead of fixing bugs | Publish public roadmap; weight priority by revenue at risk | Medium |
The team selected the top 3 high-priority initiatives and implemented them over 12 weeks:
- 30/60/90-day check-in program -- Structured touchpoints with usage benchmarks. Customers who completed all three check-ins had 74% lower churn than those who missed even one.
- Role-based simplified views -- Reduced the feature surface area visible to non-admin users by 60%. Employee adoption (measured by weekly logins) increased from 23% to 51%.
- Exit survey and save team -- Routed 38% of cancellation attempts to a save team with authority to offer configuration help, training, or temporary discounts. The save team recovered 44% of at-risk accounts.
Over 6 months, monthly churn dropped from 6.2% to 3.8% -- a 39% reduction that retained an additional $1.4M in ARR. The reverse format was critical because it surfaced failure modes (complexity, missing post-onboarding follow-up) that direct ideation had missed.
5. Round-Robin Brainstorming#
Round-robin gives each participant a turn to contribute one idea, going around the circle until the group runs out of new ideas. It is the simplest structured method and works well when you need participation from everyone but lack time for a full workshop. Sessions typically run 15-20 minutes with groups of 4-8. The constraint of one-idea-per-turn forces participants to listen and build rather than wait to pitch a pre-formed idea.
Best for: Quick sessions, small groups, ensuring introverts contribute equally.
6. Affinity Diagramming#
Affinity diagramming is a convergent technique that organizes a large volume of unstructured ideas into natural clusters. Generate ideas using any method above (each on a separate card), silently sort them into groups based on natural affinity, label each cluster with a theme header, then prioritize clusters -- not individual ideas -- for further development.
Best for: Post-brainstorm synthesis, organizing qualitative research, grouping stakeholder feedback. For prioritizing those clusters, a decision matrix or prioritization framework provides a systematic next step.
Continue reading: Agenda Slide PowerPoint · Flowchart in PowerPoint · Pitch Deck Guide
Free consulting slide templates
SWOT, competitive analysis, KPI dashboards, and more — ready-made PowerPoint templates built to consulting standards.
Method Effectiveness by Problem Type#
Based on outcomes tracked across 50+ facilitated sessions, here is how each method performs by problem type:
| Problem Type | Best Method | Why It Works | Typical Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| New product ideation | Brainwriting 6-3-5 | Volume of raw ideas; cross-pollination through rotation | 80-108 entries per session; 5-8 viable concepts after clustering |
| Existing product improvement | SCAMPER | Systematic triggers prevent fixation on obvious changes | 14-21 ideas across 7 triggers; 3-5 high-impact modifications |
| Reducing failures or churn | Reverse Brainstorming | Inversion surfaces hidden failure modes direct thinking misses | 15-25 failure modes; 6-10 actionable inversions |
| Problem scoping and exploration | Mind Mapping | Visual structure reveals gaps and cross-branch connections | 30-50 nodes; 4-6 investigation threads |
| Quick alignment sessions | Round-Robin | Equal voice in under 20 minutes | 15-30 ideas; useful for priority-setting meetings |
| Post-ideation synthesis | Affinity Diagramming | Silent clustering reveals natural theme hierarchy | 5-9 theme clusters from 50-100+ raw ideas |
General rule: Use brainwriting or round-robin for divergent ideation, then affinity diagramming for convergent synthesis. Layer SCAMPER on top when you need to push further on a specific cluster.
Running a 75-Minute Workshop#
This blueprint uses brainwriting for divergent ideation and affinity diagramming for synthesis, optimized for 6-8 participants.
Step 1: Frame the Problem (5 min) -- Write a specific, bounded problem statement. Not "How do we grow revenue?" but "What are 10 ways to increase mid-market ACV by 15% without adding headcount?"
Step 2: Silent Brainwriting (25 min) -- Run 5 rounds of the 6-3-5 method. No talking. Expect 70-90 usable entries with roughly 30% overlap (repeated themes signal strength).
Step 3: Cluster and Label (15 min) -- Transfer ideas to cards, silently sort into affinity clusters. No predefined categories. Typically produces 5-9 clusters.
Step 4: Prioritize (15 min) -- Give each participant 3-5 dot votes for highest-impact clusters. The top 2-3 become focus areas. For rigorous evaluation, use a decision matrix or stakeholder analysis.
Step 5: Assign Owners (5 min) -- Each winning cluster gets a named owner, a deliverable, and a deadline. Sessions without assigned owners produce zero follow-through 90% of the time.
Common Brainstorming Mistakes#
Evaluating during divergent phases. Even "that's a great idea" anchors the group. Post a visible "no judgment" sign and enforce it, as IDEO's design thinking methodology emphasizes.
Letting senior voices anchor. When the VP shares first, the room orbits their idea. Use brainwriting so contributions are anonymous, or have leaders join only during evaluation.
Skipping convergence. Eighty ideas with no clustering, no votes, and no owners is not an outcome. Always schedule affinity diagramming and dot-voting.
Oversized groups. Beyond 8 participants, split into parallel tables of 6 and merge results during clustering.
Key Takeaways#
- Choose your brainstorming template based on group size, problem type, and whether you are generating new ideas or improving existing ones
- Brainwriting produced 54 entries and 2 market-ready product concepts in a single 30-minute session for a snack food company
- SCAMPER systematically improved a SaaS pricing model, increasing average contract value by 31% and deal close rate from 18% to 29%
- Reverse brainstorming uncovered hidden churn drivers that direct ideation missed, reducing monthly churn from 6.2% to 3.8%
- Keep groups between 6-8 participants for maximum idea quality; split larger groups into parallel tables
- Every brainstorming session must end with prioritized clusters, assigned owners, and deadlines -- not just a list of ideas
- For visualizing your brainstorming output, the Mind Map Template provides a ready-made layout that maps directly to the mind mapping method above
Related Guides#
- Strategic Frameworks Guide -- The complete toolkit of consulting frameworks for strategy and analysis
- Decision Matrix Guide -- For systematically evaluating ideas after brainstorming
- How to Prioritize Tasks -- Prioritization frameworks that complement brainstorming output
- Stakeholder Mapping -- Map stakeholder influence before workshopping solutions
Build consulting slides in seconds
Describe what you need. AI generates structured, polished slides — charts and visuals included.
Try Free